Readdir rm -rf graphs
From Linux NFS
(Difference between revisions)
(→NFS v4) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
=== NFS v3 === | === NFS v3 === | ||
* [[File:v3_rm_rf_noplus_real.jpg]] | * [[File:v3_rm_rf_noplus_real.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** Without readdir plus, an unmodified 2.6.38 kernel takes longer to remove a large directory than the other kernels | ||
* [[File:v3_rm_rf_plus_real.jpg]] | * [[File:v3_rm_rf_plus_real.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** Using readdir plus removes large directories faster than using a simple readdir. | ||
| + | |||
=== NFS v4 === | === NFS v4 === | ||
* [[File:v4_rm_rf_noplus_real.jpg]] | * [[File:v4_rm_rf_noplus_real.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** Kernels perform the same without readdir plus | ||
* [[File:v4_rm_rf_plus_real.jpg]] | * [[File:v4_rm_rf_plus_real.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** With readdir plus enabled, the kernels take about the same amount of time to remove the directory. | ||
== Sys == | == Sys == | ||
=== NFS v3 === | === NFS v3 === | ||
* [[File:v3_rm_rf_noplus_sys.jpg]] | * [[File:v3_rm_rf_noplus_sys.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** The command takes about the same amount of kernel time for each tested kernel. | ||
* [[File:v3_rm_rf_plus_sys.jpg]] | * [[File:v3_rm_rf_plus_sys.jpg]] | ||
| + | * Using readdir plus decreases the kernel time needed to complete the command | ||
| + | |||
=== NFS v4 === | === NFS v4 === | ||
* [[File:v4_rm_rf_noplus_sys.jpg]] | * [[File:v4_rm_rf_noplus_sys.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** Tested kernels use about the same amount of kernel time to complete the command. | ||
* [[File:v4_rm_rf_plus_sys.jpg]] | * [[File:v4_rm_rf_plus_sys.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** 2.6.36 kernels use less kernel time than 2.6.38 kernels. | ||
== RPC ops == | == RPC ops == | ||
=== NFS v3 === | === NFS v3 === | ||
* [[File:v3_rm_rf_noplus_rpc.jpg]] | * [[File:v3_rm_rf_noplus_rpc.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** The tested kernels use about the same number of RPC operations. | ||
* [[File:v3_rm_rf_plus_rpc.jpg]] | * [[File:v3_rm_rf_plus_rpc.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** Using readdir plus results in fewer RPC operations to remove the directory | ||
| + | |||
=== NFS v4 === | === NFS v4 === | ||
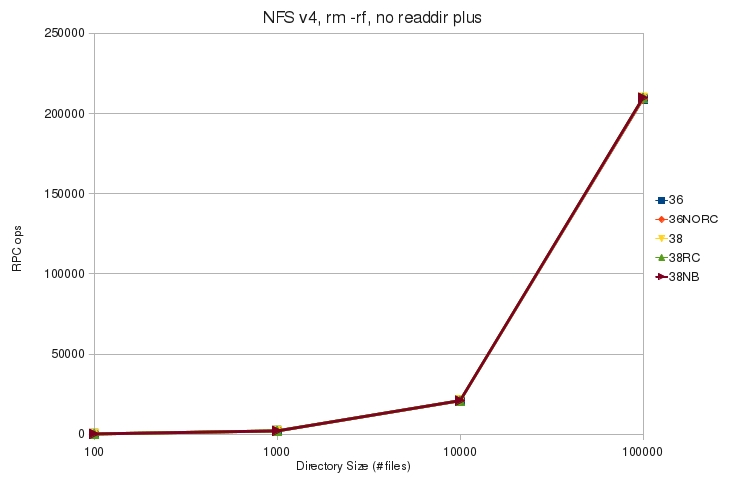
* [[File:v4_rm_rf_noplus_rpc.jpg]] | * [[File:v4_rm_rf_noplus_rpc.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** All tested kernels issue the same number of RPC operations to remove directories | ||
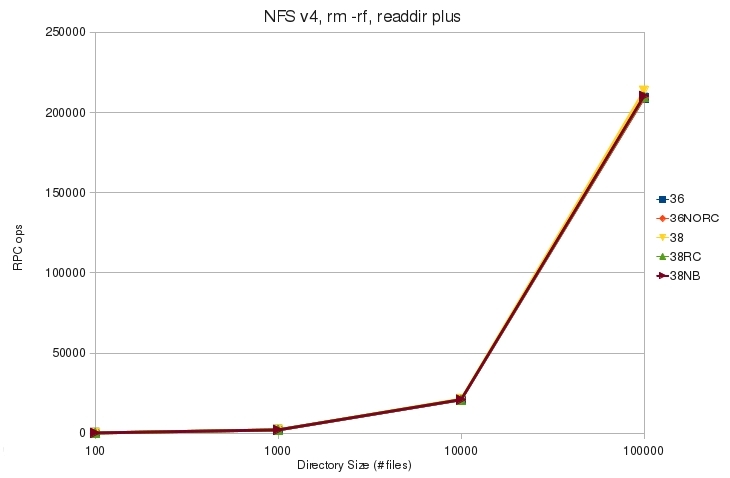
* [[File:v4_rm_rf_plus_rpc.jpg]] | * [[File:v4_rm_rf_plus_rpc.jpg]] | ||
| + | ** All tested kernels issue almost the same number of RPC operations to remove directories | ||
Latest revision as of 18:42, 7 April 2011
36: Linux 2.6.36
36NORC: Linux 2.6.36 (without readdir cap)
38: Linux 2.6.38
38RC: Linux 2.6.38 (with readdir cap added back)
38NB: Linux 2.6.38 (with Neil Brown's patch and loop detection)
Contents |
Real
NFS v3
-
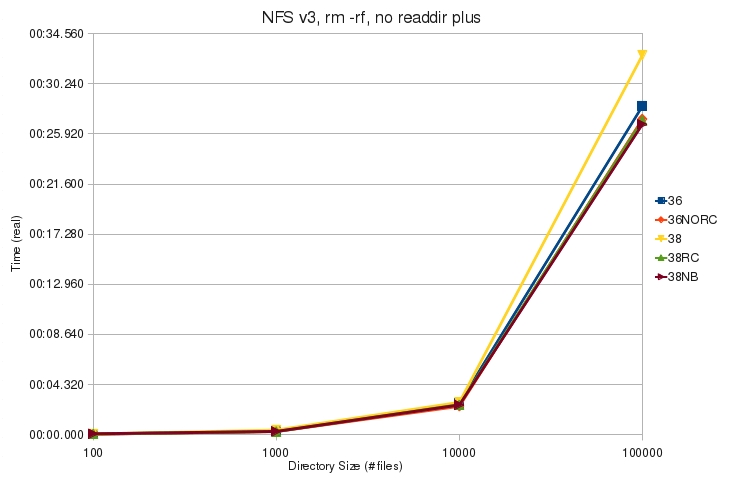
- Without readdir plus, an unmodified 2.6.38 kernel takes longer to remove a large directory than the other kernels
-
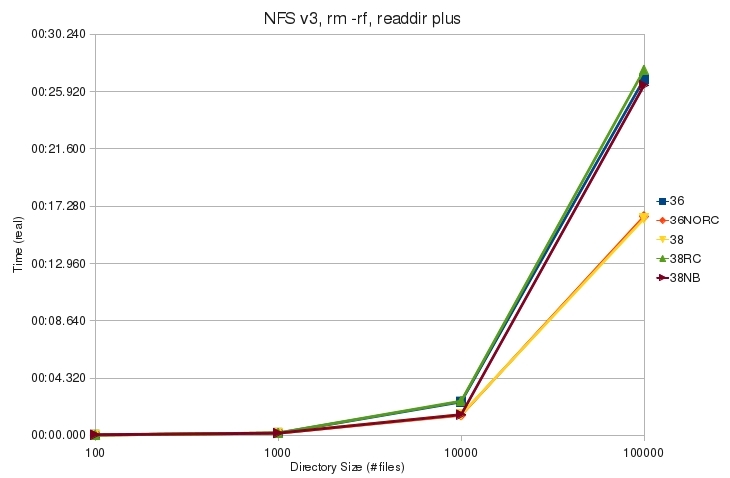
- Using readdir plus removes large directories faster than using a simple readdir.
NFS v4
-
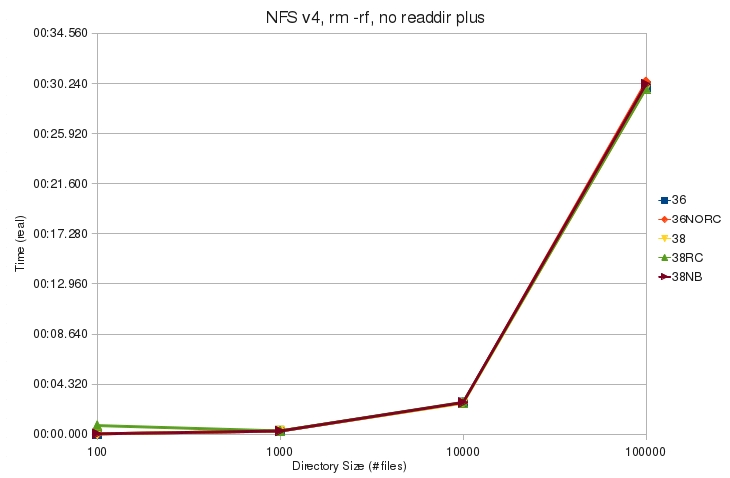
- Kernels perform the same without readdir plus
-
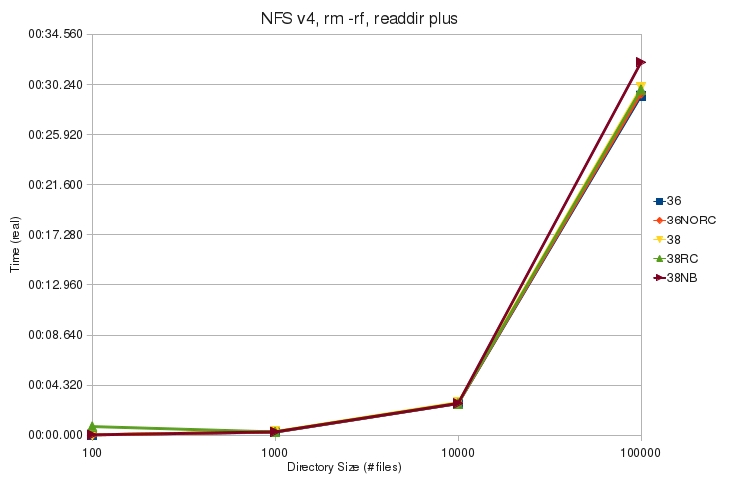
- With readdir plus enabled, the kernels take about the same amount of time to remove the directory.
Sys
NFS v3
-
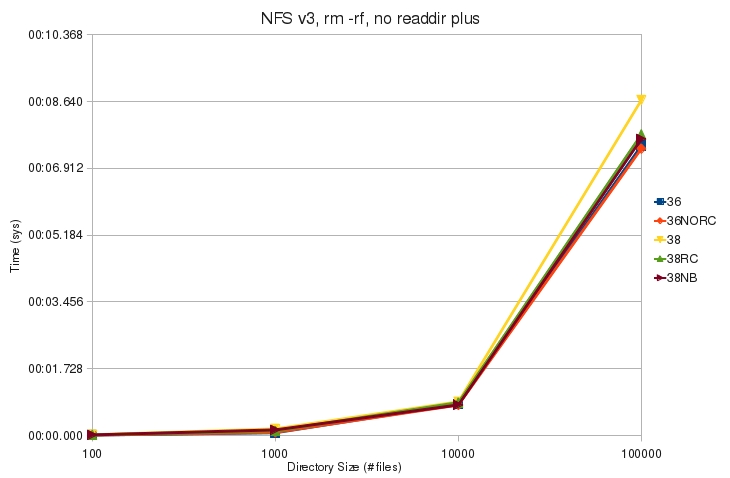
- The command takes about the same amount of kernel time for each tested kernel.
-
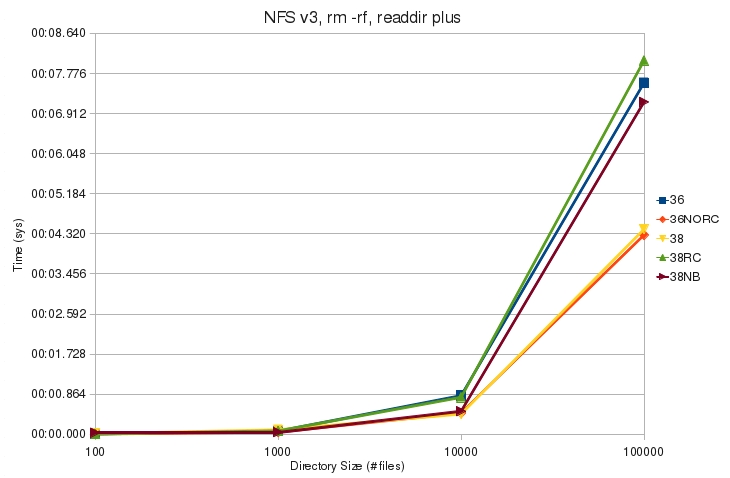
- Using readdir plus decreases the kernel time needed to complete the command
NFS v4
-

- Tested kernels use about the same amount of kernel time to complete the command.
-
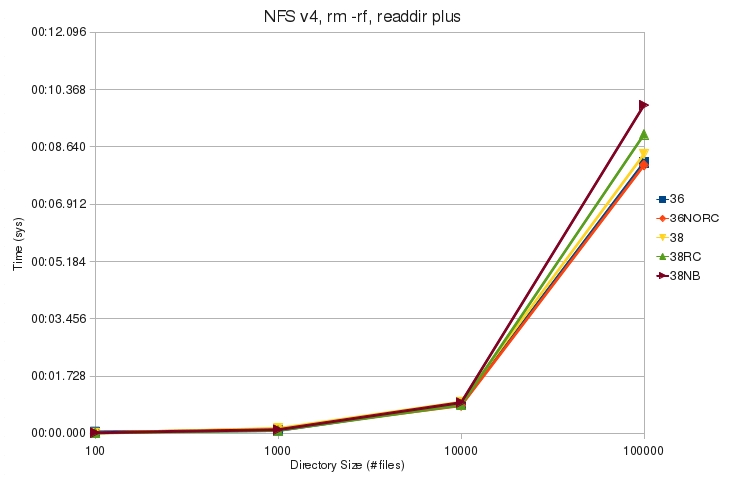
- 2.6.36 kernels use less kernel time than 2.6.38 kernels.
RPC ops
NFS v3
-
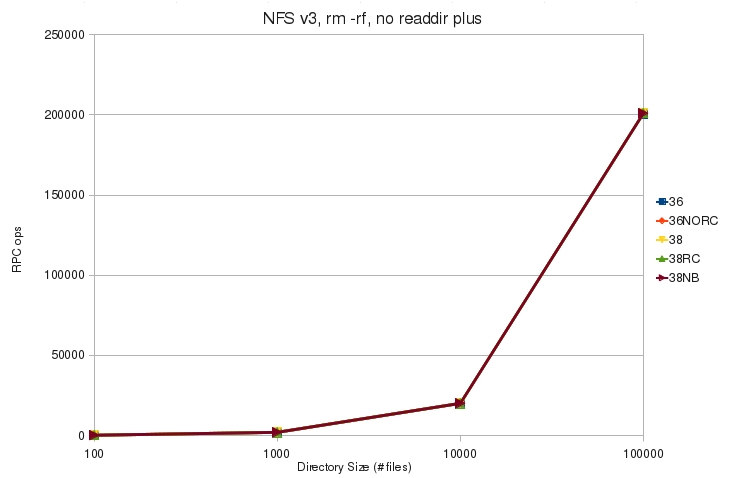
- The tested kernels use about the same number of RPC operations.
-
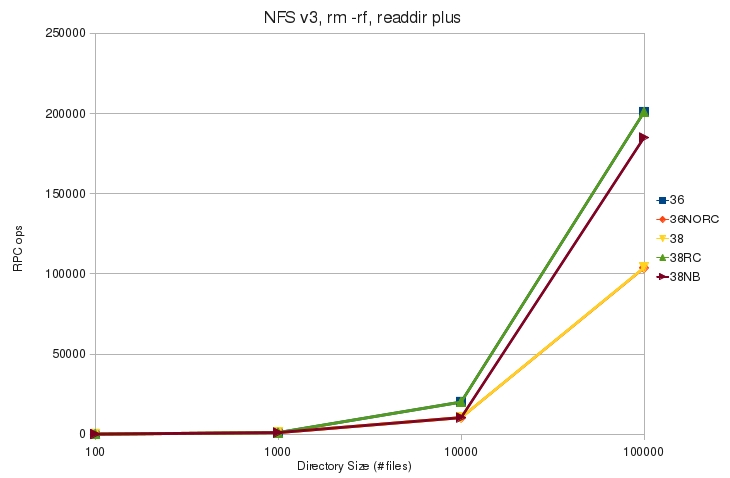
- Using readdir plus results in fewer RPC operations to remove the directory